The Technical Standard Positioning to Transform Cross-Border Payments
How the X9 Standard Payment QR Code could become the infrastructure layer that finally connects the world's fragmented instant payment systems
The global payments landscape is approaching an inflection point. While instant payment systems have proliferated across major economies—India's UPI processing 12 billion transactions monthly, Brazil's PIX handling 5 billion, and the U.S. Federal Reserve's FedNow gaining adoptio n—these systems remain largely isolated from one another.
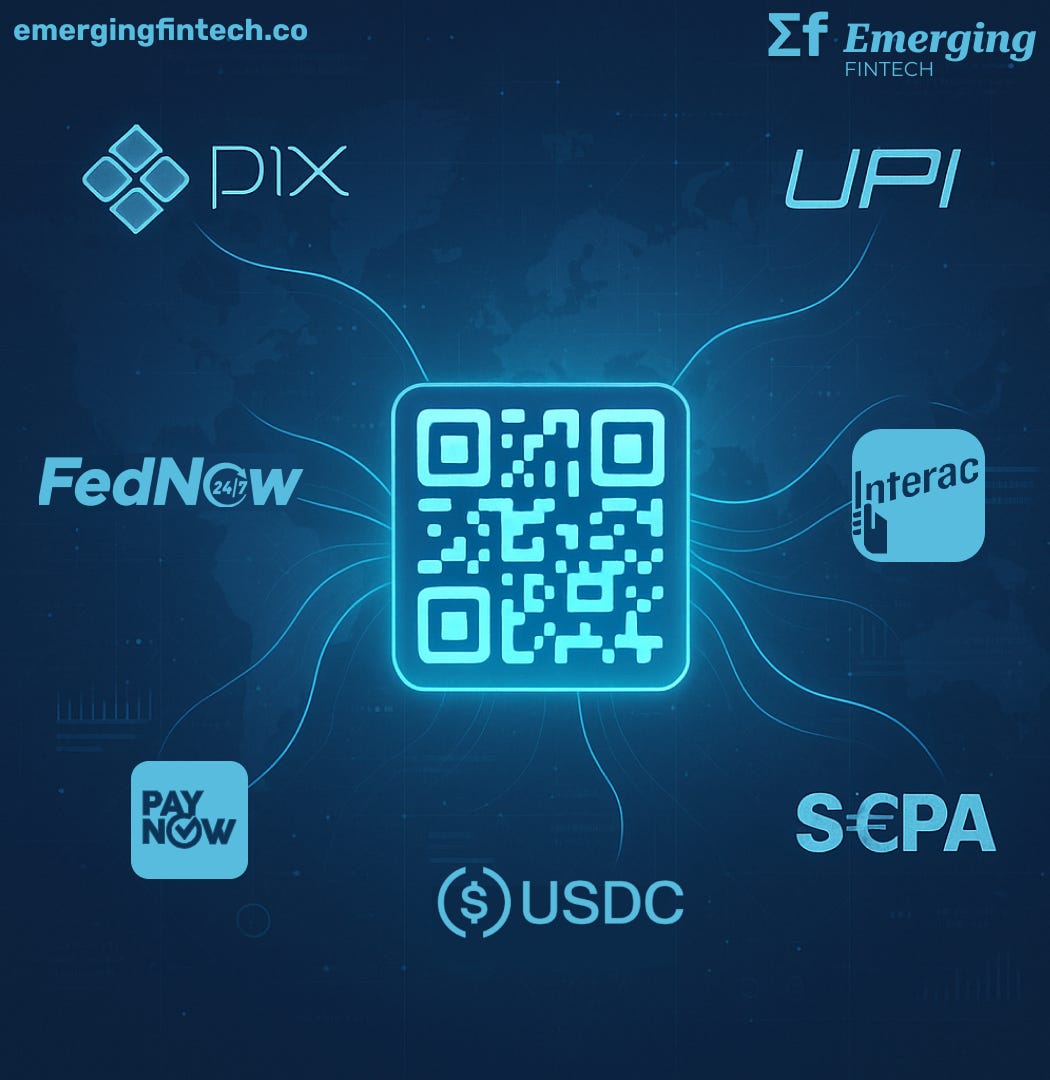
A new technical standard being developed by the Accredited Standards Committee X9 could change that. The X9 Standard Payment QR Code, currently in development since August 2024, aims to create a universal protocol for payment requests that works across any rail, any currency, and any jurisdiction. Matera CEO Carlos Netto recently outlined his vision for how this standard could enable truly global payment interoperability, but the broader implications extend far beyond any single company's perspective.
The standard represents more than incremental innovation. It could fundamentally alter competitive dynamics in an industry where geographic expansion has traditionally required years of integration work and regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
The Scale of Payment Fragmentation
The disparity in instant payment adoption reveals the extent of global fragmentation. India processes over 12 billion instant payments monthly through UPI, while Brazil handles 5 billion via PIX. In contrast, the United States—despite having the world's largest economy—processes just 30 million instant payments monthly through its newer FedNow system.
This fragmentation creates significant friction for cross-border commerce. Account-to-Account (A2A) payment volumes are projected to grow from $1.7 trillion in 2024 to $5.7 trillion by 2030, according to Juniper Research. However, current growth is constrained by the complexity of connecting disparate payment systems across borders.
Consider the technical challenges facing a merchant seeking to accept payments globally today. Supporting customers in Brazil requires PIX integration. Serving Indian customers demands UPI compatibility. Accepting payments from European customers requires SEPA connectivity. Each integration involves separate APIs, compliance requirements, and settlement processes.
The X9 Standard proposes to solve this through what amounts to a universal translation layer. A single payment request could simultaneously offer multiple settlement options—PIX for Brazilian customers, UPI for Indian users, FedNow for Americans, and USDC on blockchain networks for customers in regions lacking advanced payment infrastructure.
Infrastructure Convergence
Several technological and regulatory developments are creating the foundation for this type of interoperability. The European Union's SEPA Instant regulation, which mandated real-time payment capabilities by January 2025, has accelerated instant payment adoption across 27 countries. India's UPI has begun establishing bilateral connections with other national payment systems, including Singapore's PayNow and France's Lyra network.
Meanwhile, stablecoin infrastructure has matured to the point where USDC transactions on networks like Polygon or Solana settle faster and cheaper than traditional correspondent banking arrangements. The X9 Standard's rail-agnostic approach means these blockchain-based settlement options receive equal treatment alongside traditional banking rails.
This convergence creates interesting dynamics for financial institutions. Banks implementing X9 compatibility early could offer merchants significantly enhanced value propositions—the ability to accept payments from customers worldwide without the traditional complexity of multi-rail integration.
Competitive Implications
The standard threatens to commoditize what has been a key competitive advantage for payment processors: the ability to navigate integration complexity. Companies like Stripe built significant market positions by offering "one API" access to multiple payment methods. PayPal's cross-border payment revenues depend partly on the difficulty of alternative international transfer methods.
When payment requests can automatically include multiple settlement options through a standardized protocol, the value of proprietary integration platforms diminishes. Any bank or fintech company supporting the X9 Standard could theoretically offer global payment acceptance capabilities.
This shift could be particularly significant for emerging market financial institutions. A Nigerian fintech optimized for local mobile money could suddenly accept payments from European customers via SEPA Instant or American customers through FedNow—without building separate integrations for each market.
The pattern extends beyond payment processors to adjacent services. Fraud detection companies, reconciliation software providers, and compliance platforms that align with X9 Standard architecture gain automatic global scalability. Those that don't risk being limited to regional markets while competitors achieve worldwide reach.
The Stablecoin Integration
Perhaps the most significant aspect of the X9 Standard is its treatment of blockchain-based payment rails as equivalent to traditional banking infrastructure. For merchants, this creates unprecedented optionality in how they receive payments.
When a payment request automatically includes both traditional bank settlement options and stablecoin alternatives like USDC, customers can choose based on speed, cost, and convenience rather than technical complexity. A customer in a country with limited banking infrastructure might prefer to pay with USDC on a public blockchain, while another customer might use their domestic instant payment system.
This integration could accelerate mainstream adoption of blockchain-based payments by removing the technical barriers that currently limit their use to crypto-native users. When paying with stablecoins becomes as simple as scanning a QR code and selecting from available options, the distinction between "traditional" and "crypto" payments becomes largely irrelevant to the user experience.
Network Effects and Adoption
The success of the X9 Standard depends on achieving critical mass among financial institutions, merchants, and application developers. Network effects work strongly in favor of early adopters—each additional participant increases the value of the network for all existing participants.
Banks implementing X9 support first gain access to globally-minded merchants who prioritize international customer reach. Merchants adopting X9-compatible payment systems access customer bases previously unreachable due to payment friction. Software developers building X9 support into their applications create products that become more valuable as network adoption increases.
The timing appears favorable for rapid adoption. Major instant payment systems are already operational or expanding globally. Regulatory frameworks for real-time payments are becoming standardized. Stablecoin infrastructure has proven capable of handling significant transaction volumes.
Strategic Considerations
The X9 Standard development process remains open to industry participation, with the committee actively seeking input from financial institutions, merchants, and payment service providers. Companies engaging with the standard now can influence its final specifications while positioning for first-mover advantages.
The alternative is potentially costly. As global payment interoperability improves through standardization, companies limited to regional payment capabilities may find themselves competing against organizations with automatic worldwide reach. The competitive disadvantage could prove difficult to overcome, particularly for companies in smaller markets.
Traditional payment industry leaders face more complex strategic decisions. Their existing advantages in areas like fraud detection, customer experience, and financial product innovation remain valuable. However, competitive moats built around payment integration complexity may erode as standardization reduces technical barriers.
Market Transformation
The broader implications extend beyond individual company strategies to the structure of global commerce itself. When payment friction between countries decreases significantly, it could accelerate international trade, particularly for smaller businesses that currently find cross-border commerce prohibitively complex.
Global cashless payment volumes are projected to increase by more than 80% from 2020 to 2025, reaching nearly 1.9 trillion transactions. The X9 Standard's potential to reduce cross-border payment complexity could accelerate this growth while creating substantial value for companies positioned correctly.
The protocol represents infrastructure innovation rather than application innovation—similar to how TCP/IP enabled the internet's applications rather than creating them directly. The companies that benefit most will likely be those that recognize this infrastructure shift early and build their strategies accordingly.
As the X9 Standard development continues through 2025, the payments industry faces a fundamental question: whether to embrace standardization that reduces competitive barriers but expands market opportunities, or to preserve existing advantages while potentially missing the global interoperability transition.
The answer will likely determine which companies define the next phase of global payments infrastructure.
Sources
Primary Industry Data:
Accredited Standards Committee X9. "X9 Launches Effort to Create Payment QR Code Standard." August 13, 2024.
Accredited Standards Committee X9. "X9 Publishes Standard for QR Code Protection Using Cryptography." January 7, 2025.
Juniper Research. "Account-to-Account Payments: Market Forecasts, Competitor Leaderboard & Future Opportunities 2024-2030." 2024.
Payment System Statistics:
Reserve Bank of India. "Annual Report on Payment and Settlement Systems 2023-24." RBI, 2024.
Banco Central do Brasil. "PIX Statistics and Transaction Data." BCB, 2024.
Federal Reserve Banks. "FedNow Service Adoption and Transaction Volume Reports." Federal Reserve, 2024-2025.
Market Analysis and Projections:
McKinsey & Company. "Global Payments in 2024: Simpler Interfaces, Complex Reality." October 2024.
PwC and Strategy&. "Payments 2025 and Beyond: Global Cashless Payment Volume Analysis." 2024.
Capgemini. "World Payments Report 2025." March 2025.
Regulatory and Infrastructure Development:
European Central Bank. "SEPA Instant Credit Transfer Scheme Implementation." ECB, 2024.
European Payments Council. "Verification of Payee Scheme Implementation Guidelines." EPC, 2024.
Mastercard. "10 Top Payment Trends for 2025 and Beyond." December 2024.
Cross-Border Payment Innovation:
Netto, Carlos. "The Future of Global Payments: Push, Real-Time, and Open." LinkedIn, June 29, 2025.
Visa. "From AI to RTP: Top Trends Shaping 2025 Payments." Corporate Insights, 2025.
Red Compass Labs. "2025 Payments Trends: What's in Store?" January 29, 2025.
Blockchain and Stablecoin Infrastructure:
Digital Transactions. "X9 Issues QR Code Standard and Other Digital Transactions News." January 7, 2025.
American Banker. "A Unified Standard for QR Codes is the Next Step in Real-Time Payments." October 24, 2024.
This analysis is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. Always conduct your own research and consult with qualified financial professionals before making investment decisions.